 |
| June 01, 2021 | Volume 17 Issue 21 |
Electrical/Electronic News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Intro to reed switches, magnets, magnetic fields
 This brief introductory video on the DigiKey site offers tips for engineers designing with reed switches. Dr. Stephen Day, Ph.D. from Coto Technology gives a solid overview on reed switches -- complete with real-world application examples -- and a detailed explanation of how they react to magnetic fields.
This brief introductory video on the DigiKey site offers tips for engineers designing with reed switches. Dr. Stephen Day, Ph.D. from Coto Technology gives a solid overview on reed switches -- complete with real-world application examples -- and a detailed explanation of how they react to magnetic fields.
View the video.
Bi-color LEDs to light up your designs
 Created with engineers and OEMs in mind, SpectraBright Series SMD RGB and Bi-Color LEDs from Visual Communi-cations Company (VCC) deliver efficiency, design flexibility, and control for devices in a range of industries, including mil-aero, automated guided vehicles, EV charging stations, industrial, telecom, IoT/smart home, and medical. These 50,000-hr bi-color and RGB options save money and space on the HMI, communicating two or three operating modes in a single component.
Created with engineers and OEMs in mind, SpectraBright Series SMD RGB and Bi-Color LEDs from Visual Communi-cations Company (VCC) deliver efficiency, design flexibility, and control for devices in a range of industries, including mil-aero, automated guided vehicles, EV charging stations, industrial, telecom, IoT/smart home, and medical. These 50,000-hr bi-color and RGB options save money and space on the HMI, communicating two or three operating modes in a single component.
Learn more.
All about slip rings: How they work and their uses
 Rotary Systems has put together a really nice basic primer on slip rings -- electrical collectors that carry a current from a stationary wire into a rotating device. Common uses are for power, proximity switches, strain gauges, video, and Ethernet signal transmission. This introduction also covers how to specify, assembly types, and interface requirements. Rotary Systems also manufactures rotary unions for fluid applications.
Rotary Systems has put together a really nice basic primer on slip rings -- electrical collectors that carry a current from a stationary wire into a rotating device. Common uses are for power, proximity switches, strain gauges, video, and Ethernet signal transmission. This introduction also covers how to specify, assembly types, and interface requirements. Rotary Systems also manufactures rotary unions for fluid applications.
Read the overview.
Seifert thermoelectric coolers from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct has added new high-quality and efficient stainless steel Seifert 340 BTU/H thermoelectric coolers with 120-V and 230-V power options. Thermoelectric coolers from Seifert use the Peltier Effect to create a temperature difference between the internal and ambient heat sinks, making internal air cooler while dissipating heat into the external environment. Fans assist the convective heat transfer from the heat sinks, which are optimized for maximum flow.
Automation-Direct has added new high-quality and efficient stainless steel Seifert 340 BTU/H thermoelectric coolers with 120-V and 230-V power options. Thermoelectric coolers from Seifert use the Peltier Effect to create a temperature difference between the internal and ambient heat sinks, making internal air cooler while dissipating heat into the external environment. Fans assist the convective heat transfer from the heat sinks, which are optimized for maximum flow.
Learn more.
EMI shielding honeycomb air vent panel design
 Learn from the engineering experts at Parker how honeycomb air vent panels are used to help cool electronics with airflow while maintaining electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Topics include: design features, cell size and thickness, platings and coatings, and a stacked design called OMNI CELL construction. These vents can be incorporated into enclosures where EMI radiation and susceptibility is a concern or where heat dissipation is necessary. Lots of good info.
Learn from the engineering experts at Parker how honeycomb air vent panels are used to help cool electronics with airflow while maintaining electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Topics include: design features, cell size and thickness, platings and coatings, and a stacked design called OMNI CELL construction. These vents can be incorporated into enclosures where EMI radiation and susceptibility is a concern or where heat dissipation is necessary. Lots of good info.
Read the Parker blog.
What is 3D-MID? Molded parts with integrated electronics from HARTING
 3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
3D-MID (three-dimensional mechatronic integrated devices) technology combines electronic and mechanical functionalities into a single, 3D component. It replaces the traditional printed circuit board and opens up many new opportunities. It takes injection-molded parts and uses laser-direct structuring to etch areas of conductor structures, which are filled with a copper plating process to create very precise electronic circuits. HARTING, the technology's developer, says it's "Like a PCB, but 3D." Tons of possibilities.
View the video.
Loss-free conversion of 3D/CAD data
 CT CoreTech-nologie has further developed its state-of-the-art CAD converter 3D_Evolution and is now introducing native interfaces for reading Solidedge and writing Nx and Solidworks files. It supports a wide range of formats such as Catia, Nx, Creo, Solidworks, Solidedge, Inventor, Step, and Jt, facilitating smooth interoperability between different systems and collaboration for engineers and designers in development environments with different CAD systems.
CT CoreTech-nologie has further developed its state-of-the-art CAD converter 3D_Evolution and is now introducing native interfaces for reading Solidedge and writing Nx and Solidworks files. It supports a wide range of formats such as Catia, Nx, Creo, Solidworks, Solidedge, Inventor, Step, and Jt, facilitating smooth interoperability between different systems and collaboration for engineers and designers in development environments with different CAD systems.
Learn more.
Top 5 reasons for solder joint failure
 Solder joint reliability is often a pain point in the design of an electronic system. According to Tyler Ferris at ANSYS, a wide variety of factors affect joint reliability, and any one of them can drastically reduce joint lifetime. Properly identifying and mitigating potential causes during the design and manufacturing process can prevent costly and difficult-to-solve problems later in a product lifecycle.
Solder joint reliability is often a pain point in the design of an electronic system. According to Tyler Ferris at ANSYS, a wide variety of factors affect joint reliability, and any one of them can drastically reduce joint lifetime. Properly identifying and mitigating potential causes during the design and manufacturing process can prevent costly and difficult-to-solve problems later in a product lifecycle.
Read this informative ANSYS blog.
Advanced overtemp detection for EV battery packs
 Littelfuse has introduced TTape, a ground-breaking over-temperature detection platform designed to transform the management of Li-ion battery systems. TTape helps vehicle systems monitor and manage premature cell aging effectively while reducing the risks associated with thermal runaway incidents. This solution is ideally suited for a wide range of applications, including automotive EV/HEVs, commercial vehicles, and energy storage systems.
Littelfuse has introduced TTape, a ground-breaking over-temperature detection platform designed to transform the management of Li-ion battery systems. TTape helps vehicle systems monitor and manage premature cell aging effectively while reducing the risks associated with thermal runaway incidents. This solution is ideally suited for a wide range of applications, including automotive EV/HEVs, commercial vehicles, and energy storage systems.
Learn more.
Benchtop ionizer for hands-free static elimination
 EXAIR's Varistat Benchtop Ionizer is the latest solution for neutralizing static on charged surfaces in industrial settings. Using ionizing technology, the Varistat provides a hands-free solution that requires no compressed air. Easily mounted on benchtops or machines, it is manually adjustable and perfect for processes needing comprehensive coverage such as part assembly, web cleaning, printing, and more.
EXAIR's Varistat Benchtop Ionizer is the latest solution for neutralizing static on charged surfaces in industrial settings. Using ionizing technology, the Varistat provides a hands-free solution that requires no compressed air. Easily mounted on benchtops or machines, it is manually adjustable and perfect for processes needing comprehensive coverage such as part assembly, web cleaning, printing, and more.
Learn more.
LED light bars from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct adds CCEA TRACK-ALPHA-PRO series LED light bars to expand their offering of industrial LED fixtures. Their rugged industrial-grade anodized aluminum construction makes TRACKALPHA-PRO ideal for use with medium to large-size industrial machine tools and for use in wet environments. These 120 VAC-rated, high-power LED lights provide intense, uniform lighting, with up to a 4,600-lumen output (100 lumens per watt). They come with a standard bracket mount that allows for angle adjustments. Optional TACLIP mounts (sold separately) provide for extra sturdy, vibration-resistant installations.
Automation-Direct adds CCEA TRACK-ALPHA-PRO series LED light bars to expand their offering of industrial LED fixtures. Their rugged industrial-grade anodized aluminum construction makes TRACKALPHA-PRO ideal for use with medium to large-size industrial machine tools and for use in wet environments. These 120 VAC-rated, high-power LED lights provide intense, uniform lighting, with up to a 4,600-lumen output (100 lumens per watt). They come with a standard bracket mount that allows for angle adjustments. Optional TACLIP mounts (sold separately) provide for extra sturdy, vibration-resistant installations.
Learn more.
World's first metalens fisheye camera
 2Pi Optics has begun commercial-ization of the first fisheye camera based on the company's proprietary metalens technology -- a breakthrough for electronics design engineers and product managers striving to miniaturize the tiny digital cameras used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), AR/VR, UAVs, robotics, and other industrial applications. This camera can operate at different wavelengths -- from visible, to near IR, to longer IR -- and is claimed to "outperform conventional refractive, wide-FOV optics in all areas: size, weight, performance, and cost."
2Pi Optics has begun commercial-ization of the first fisheye camera based on the company's proprietary metalens technology -- a breakthrough for electronics design engineers and product managers striving to miniaturize the tiny digital cameras used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), AR/VR, UAVs, robotics, and other industrial applications. This camera can operate at different wavelengths -- from visible, to near IR, to longer IR -- and is claimed to "outperform conventional refractive, wide-FOV optics in all areas: size, weight, performance, and cost."
Learn more.
Orbex offers two fiber optic rotary joint solutions
 Orbex Group announces its 700 Series of fiber optic rotary joint (FORJ) assemblies, supporting either single or multi-mode operation ideal for high-speed digital transmission over long distances. Wavelengths available are 1,310 or 1,550 nm. Applications include marine cable reels, wind turbines, robotics, and high-def video transmission. Both options feature an outer diameter of 7 mm for installation in tight spaces. Construction includes a stainless steel housing.
Orbex Group announces its 700 Series of fiber optic rotary joint (FORJ) assemblies, supporting either single or multi-mode operation ideal for high-speed digital transmission over long distances. Wavelengths available are 1,310 or 1,550 nm. Applications include marine cable reels, wind turbines, robotics, and high-def video transmission. Both options feature an outer diameter of 7 mm for installation in tight spaces. Construction includes a stainless steel housing.
Learn more.
Mini tunnel magneto-resistance effect sensors
 Littelfuse has released its highly anticipated 54100 and 54140 mini Tunnel Magneto-Resistance (TMR) effect sensors, offering unmatched sensitivity and power efficiency. The key differentiator is their remarkable sensitivity and 100x improvement in power efficiency compared to Hall Effect sensors. They are well suited for applications in position and limit sensing, RPM measurement, brushless DC motor commutation, and more in various markets including appliances, home and building automation, and the industrial sectors.
Littelfuse has released its highly anticipated 54100 and 54140 mini Tunnel Magneto-Resistance (TMR) effect sensors, offering unmatched sensitivity and power efficiency. The key differentiator is their remarkable sensitivity and 100x improvement in power efficiency compared to Hall Effect sensors. They are well suited for applications in position and limit sensing, RPM measurement, brushless DC motor commutation, and more in various markets including appliances, home and building automation, and the industrial sectors.
Learn more.
Panasonic solar and EV components available from Newark
 Newark has added Panasonic Industry's solar inverters and EV charging system components to their power portfolio. These best-in-class products help designers meet the growing global demand for sustainable and renewable energy mobility systems. Offerings include film capacitors, power inductors, anti-surge thick film chip resistors, graphite thermal interface materials, power relays, capacitors, and wireless modules.
Newark has added Panasonic Industry's solar inverters and EV charging system components to their power portfolio. These best-in-class products help designers meet the growing global demand for sustainable and renewable energy mobility systems. Offerings include film capacitors, power inductors, anti-surge thick film chip resistors, graphite thermal interface materials, power relays, capacitors, and wireless modules.
Learn more.
Atoms seen at record resolution by Cornell researchers
In 2018, Cornell researchers built a high-powered detector that, in combination with an algorithm-driven process called ptychography, set a world record by tripling the resolution of a state-of-the-art electron microscope.
As successful as it was, that approach had a weakness. It only worked with ultrathin samples that were a few atoms thick. Anything thicker would cause the electrons to scatter in ways that could not be disentangled.
Now, a team, again led by David Muller, the Samuel B. Eckert Professor of Engineering, has bested its own record by a factor of two with an electron microscope pixel array detector (EMPAD) that incorporates even more sophisticated 3D reconstruction algorithms.
The resolution is so fine-tuned, the only blurring that remains is the thermal jiggling of the atoms themselves.
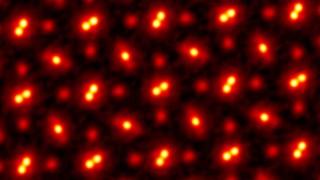
This new 2021 image shows an electron ptychographic reconstruction of a praseodymium orthoscandate (PrScO3) crystal, zoomed in 100 million times. [Credit: Cornell U. researchers]
The group's paper, "Electron Ptychography Achieves Atomic-Resolution Limits Set by Lattice Vibrations," was published May 20 in Science. The paper's lead author is postdoctoral researcher Zhen Chen.
"This doesn't just set a new record," Muller said. "It's reached a regime which is effectively going to be an ultimate limit for resolution. We basically can now figure out where the atoms are in a very easy way. This opens up a whole lot of new measurement possibilities of things we've wanted to do for a very long time. It also solves a long-standing problem -- undoing the multiple scattering of the beam in the sample, which Hans Bethe laid out in 1928 -- that has blocked us from doing this in the past."
Ptychography works by scanning overlapping scattering patterns from a material sample and looking for changes in the overlapping region.
"We're chasing speckle patterns that look a lot like those laser-pointer patterns that cats are equally fascinated by," Muller said. "By seeing how the pattern changes, we are able to compute the shape of the object that caused the pattern."
The detector is slightly defocused, blurring the beam, in order to capture the widest range of data possible. This data is then reconstructed via complex algorithms, resulting in an ultraprecise image with picometer (one-trillionth of a meter) precision.
"With these new algorithms, we're now able to correct for all the blurring of our microscope to the point that the largest blurring factor we have left is the fact that the atoms themselves are wobbling, because that's what happens to atoms at finite temperature," Muller said. "When we talk about temperature, what we're actually measuring is the average speed of how much the atoms are jiggling."
The researchers could possibly top their record again by using a material that consists of heavier atoms, which wobble less, or by cooling down the sample. But even at zero temperature, atoms still have quantum fluctuations, so the improvement would not be very large.
This latest form of electron ptychography will enable scientists to locate individual atoms in all three dimensions when they might be otherwise hidden using other imaging methods. Researchers will also be able to find impurity atoms in unusual configurations and image them and their vibrations, one at a time. This could be particularly helpful in imaging semiconductors, catalysts, and quantum materials -- including those used in quantum computing -- as well as for analyzing atoms at the boundaries where materials are joined together.
The imaging method could also be applied to thick biological cells or tissues, or even the synapse connections in the brain -- what Muller refers to as "connectomics on demand."
While the method is time-consuming and computationally demanding, it could be made more efficient with more powerful computers in conjunction with machine learning and faster detectors.
"We want to apply this to everything we do," said Muller, who co-directs the Kavli Institute at Cornell for Nanoscale Science and co-chairs the Nanoscale Science and Microsystems Engineering (NEXT Nano) Task Force, part of Cornell's Radical Collaboration initiative. "Until now, we've all been wearing really bad glasses. Now, we actually have a really good pair. Why wouldn't you want to take off the old glasses, put on the new ones, and use them all the time?"
Co-authors include Darrell Schlom, the Herbert Fisk Johnson Professor of Industrial Chemistry; Yi Jiang, Ph.D. '18 and now a beamline data scientist at Argonne National Laboratory; postdoctoral researchers Yu-Tsun Shao and Megan Holtz, Ph.D. '17; and researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute and the Leibniz Institute for Crystal Growth.
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation through Cornell's Platform for the Accelerated Realization, Analysis, and Discovery of Interface Materials (PARADIM).
Source: Cornell University
Published June 2021
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
